In this article, we will explain what decentralized exchanges (DEX) are and how they work. We will also briefly cover some of their pros and cons.
What is a Decentralized Exchange (DEX)?
In the crypto area, a DEX is a type of cryptocurrency exchange that allows users to buy and sell crypto through direct peer-to-peer transactions.
It works in a decentralized way, without relying on a central authority.
A DEX shares some similarities with a centralized exchange (CEX) as it allows customers to trade cryptocurrencies for other assets, be it fiat money or another cryptocurrency.
One major difference between the two types of exchanges is that in the case of a DEX, the third party that oversees the asset transfer and security is substituted for a distributed ledger or blockchain.
Moreover, users don’t need to give up custody of their funds, having control over them at all times.
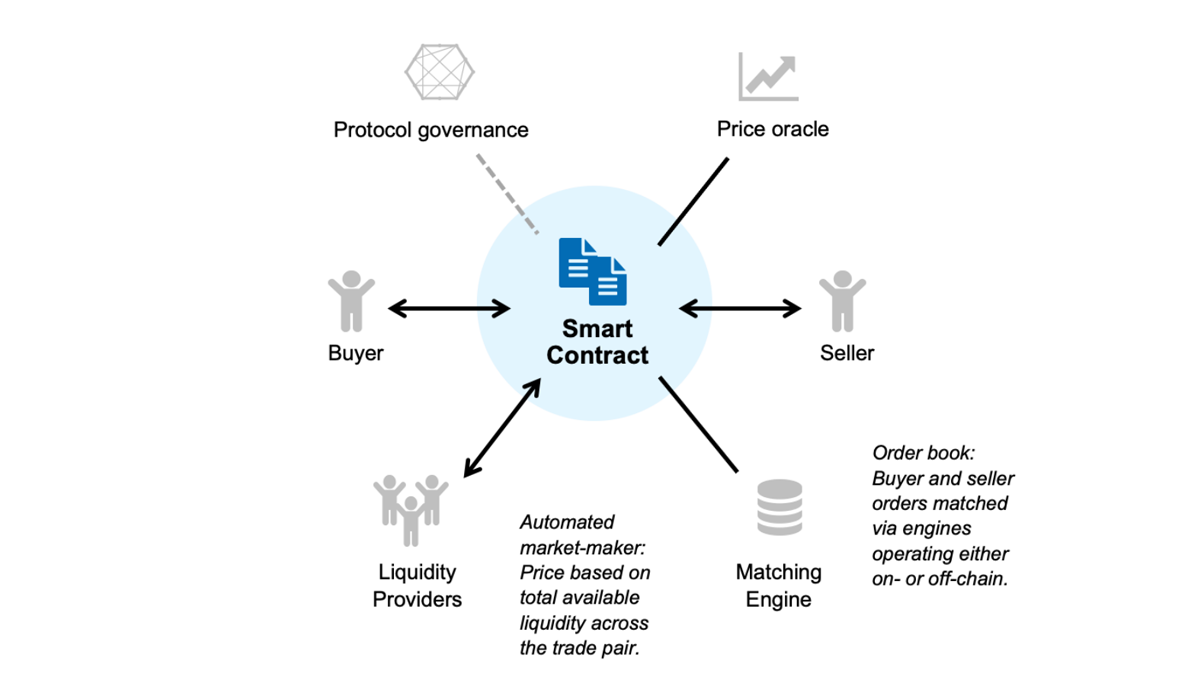
How Does a DEX Work?
A DEX operates without an intermediary for clearing transactions, and orders are executed on-chain. To facilitate trading, it relies on self-executing smart contracts.
It uses different DeFi protocols and mechanisms, such as order books, liquidity pools, AMMs, and aggregation tools.
Based on that, we can talk about different types and generations of DEXs, including:
- Order book DEXs, such as dYdX and Binance DEX; and
- Swap DEXs, such as Uniswap, Curve, SushiSwap, Balancer, Bancor, and Kyber.
Some of their components have varying degrees of decentralization, which has led even to semi-decentralized exchanges.
Pros of DEXs
DEXs come with several advantages, as follows:
- They don’t hold users’ funds, so there is no counterparty risk.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML)/Know Your Customer (KYC) compliance is not a norm in this case, and the users’ identity is not checked since they are permissionless. All that is required is a crypto-wallet.
- Since critical operations are moved onto a blockchain, the technology used eliminates single points of failure.
- Given that users don’t have to transfer their assets to an exchange, the risk of theft or loss of funds caused by hacks is reduced.
- Customers have access to a greater token variety.
Cons of DEXs
Despite their many benefits, DEXs are not free of disadvantages. Some of their cons include:
- Low trading volume and liquidity;
- No recovery ability – since users hold their private keys and there is no KYC process or way to revert a transaction, in case they get lost or stolen, the DEX cannot recover them.
- Higher transaction fees;
- Network congestion when there is a high trading volume;
- Usability – they are less user-friendly than centralized exchanges and have limited trading functionalities; and
- Price slippage.
Conclusion
To sum up, even though many decentralized exchanges have emerged in recent years, there is still room for improvement, and centralized exchanges are currently the preferred choice for many crypto traders.